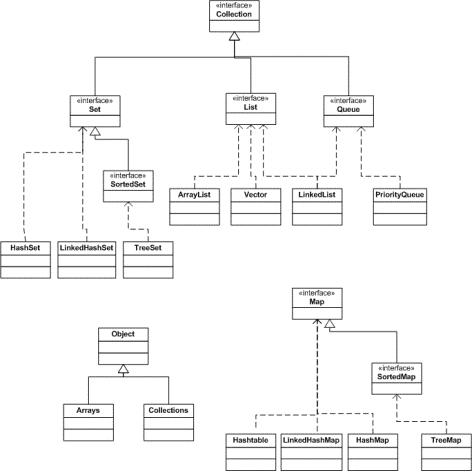
Collections are very important on SCJP exam. It’s useful to remember the following…
List
- ordered (index)
- duplicates allowed
ArrayList
- fast iteration
- fast random access; as of Java 1.4 implements
RandomAccessinterface - slower instertion and deletion
Vector
- the same as ArrayList but its metods are synchronized (therefore slower)
LinkedList
- elements are doubly linked to one another; linkage adds methods that allow adding/removing from beginning and end of the List (stacks, queues)
- fast insertion and deletion
- slower iteration
- as of Java 5 implements
java.util.Queue
Set
- can be ordered
- can be sorted
- duplicates not allowed (
eqauls())
HashSet
- unordered
- unsorted
- fast access
- uses
hashCode()of the inserted object
LinkedHashSet
- ordered HashSet (order of insertion)
- unsorted
- elements are doubly linked to one another
TreeSet
- sorted (one of two sorted Collections) – elements are kept in ascending order according to natural order
- uses Red-Block tree structure
- attempt of adding an object which doesn’t implement
compareTo()results in ClassCastException
Map
- can be ordered
- can be sorted
- duplicate keys not allowed (
eqauls()) - any class used as a key for a Map must override
hashCode()andeqauls()
HashMap
- unordered
- unsorted
- fast updates (key/value pairs)
- allow one null key and many null values
Hashtable
- synchronized HashMap (slower)
- old…
- can’t keep anything that is null
LinkedHashMap
- insertion order
- fast iteration
- slower addition and deletion
- allow one null key and many null values
TreeMap
- sorted
- can define custom order using
ComparableorComparator
Queue
- ordered by FIFO (first in – first out) or by priority
PriorityQueue
- you can create a priority-in and priority-out queue as opposed to typical FIFO
- ordered by natural order (elements sorted first will be accessed first) or according to Comparator
size()peek()– returns the highest priority element, without removingpoll()– returns the highest priority element and removes itoffer()– adds an element